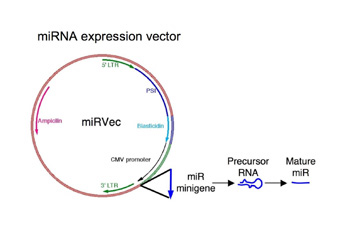
Endogenous small RNAs (miRNAs) regulate gene expression by mechanisms conserved across metazoans. While the number of verified human miRNAs is still expanding, only few have been functionally annotated. To perform genetic screens for novel functions of miRNAs we developed a library of vectors expressing the majority of cloned human miRNAs and created corresponding DNA barcode arrays.
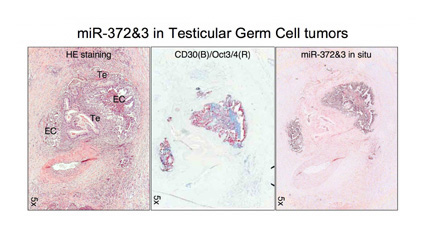
In a screen for miRNAs that cooperate with oncogenes in cellular transformation we identified miR-372 and miR-373, each permitting proliferation and tumorigenesis of primary human cells that harbor both oncogenic RAS and active wild type p53. These miRNAs neutralize p53-mediated CDK2 inhibition, most likely through direct suppression of the expression of the tumor-suppressor LATS2. We demonstrate that these miRNAs are novel oncogenes participating in the development of human testicular germ cell tumors by numbing the p53 pathway, thus allowing tumorigenic growth in the presence of wild type p53.
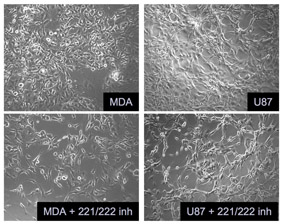
In a a novel functional genetic approach we identified miR-221 and miR-222 (miR-221&222) as potent regulators of p27Kip1, a cell cycle inhibitor and tumor suppressor. Interestingly, high miR-221 level appears in signatures of poor prognosis cancers. Using miRNA-inhibitors we demonstrated that certain cancer cell lines require high activity of miR-221 for the maintenance of low p27Kip1 levels and continuous proliferation. We show that this interaction plays a role in human glioblastoma development.